Wealth Profile Of Christ Apostolic Church (Cac)

Christ Apostolic Church (CAC) is one of the most prominent and respected Christian denominations in Nigeria. Founded in 1918, it is recognized as Nigeria’s first indigenous Pentecostal church. Over the decades, the church has expanded beyond the borders of Nigeria, establishing a strong presence in countries such as the United Kingdom, Tanzania, Spain, and several others.
While the spiritual legacy of CAC is widely known, its financial and infrastructural strength is equally notable. With thousands of branches, major properties, educational institutions, and diverse income streams, CAC has grown into a powerhouse within both the religious and socio-economic spheres of Nigeria.
In this blog post, we delve deep into the wealth profile of Christ Apostolic Church, examining how it generates revenue, manages its assets, and the challenges that come with such expansive growth.
1. Historical Foundation and Leadership Influence
Christ Apostolic Church began its journey with a spiritual revival led by Apostle Joseph Ayo Babalola. Today, the church continues to operate under a structured leadership that oversees its operations across Nigeria and abroad. The current President, Pastor S. O. Oladele, along with other key leaders like Pastor E.O. Odejobi (General Superintendent) and Prophet Hezekiah H. Oladeji (General Evangelist), play significant roles in guiding the church’s spiritual and financial direction.
Strong leadership has contributed immensely to the effective management of CAC’s wealth. Their influence is evident in the church’s strategic investments in infrastructure, education, and other sustainable projects.
2. Real Estate Holdings and Infrastructural Investments
One of the most visible indicators of CAC’s wealth is its vast real estate and infrastructural developments. These investments serve not only as worship centers but also as strategic assets contributing to the church’s financial health.
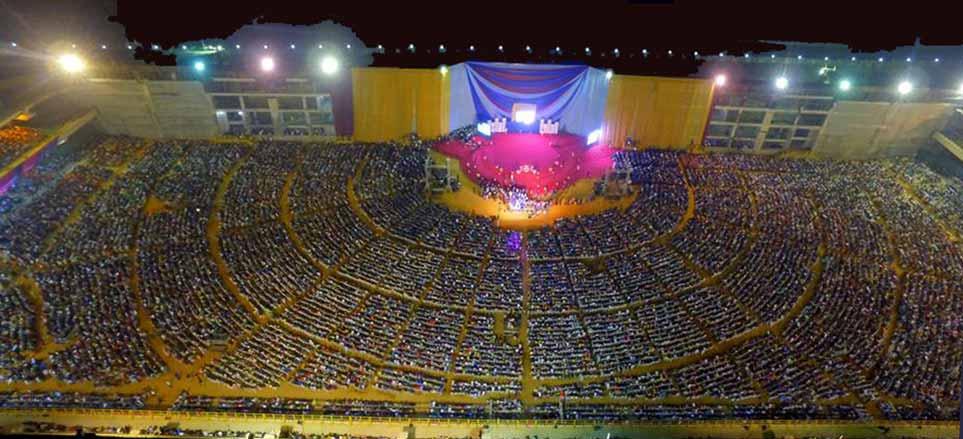
Agbala Itura Headquarters
Perhaps one of the most well-known branches of CAC is the Agbala Itura, led by Prophet Samuel Abiara. The Lagos branch features a 20,000-capacity worship auditorium, while its Oyo State location seats 25,000 people. Combined, these buildings are valued at over ₦2.5 billion. Reports indicate that monthly offerings in these branches alone can exceed ₦10 million, showcasing the financial power within the church's congregation.
Joseph Ayo Babalola International Miracle Camp
Located in Ikeji-Arakeji, Osun State, this spiritual retreat center attracts thousands of worshippers during annual conventions and special services. It stands as a symbol of the church’s deep-rooted spiritual traditions while also serving as a major revenue-generating asset during large events.
3. Educational Institutions and Human Capital Investment
CAC’s commitment to education is evident through the establishment of institutions that serve both spiritual and academic purposes. These institutions are well-funded and have become critical components of the church's legacy.
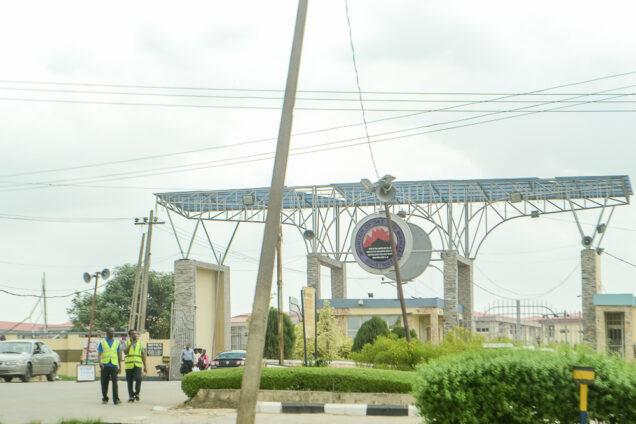
Joseph Ayo Babalola University (JABU)
Founded in 2004, JABU is Nigeria’s first entrepreneurial university and one of CAC’s most prestigious investments. Located in Osun State, the university serves thousands of students across various disciplines. Beyond academic excellence, JABU generates substantial income through tuition, research funding, and partnerships, thereby boosting the church’s financial profile.
Christ International Divinity College (CINDICO)
Another notable institution is CINDICO, affiliated with Acadia University in Canada. It serves as a theological seminary for training church leaders and missionaries. With an estimated value of over ₦100 million, CINDICO represents both a spiritual and economic investment in human capital.
4. Revenue Streams and Financial Strategies
CAC has established multiple revenue streams that contribute to its financial sustainability. While offerings and tithes remain foundational, other income sources demonstrate strategic financial planning.
Tithes and Offerings
This remains the core revenue source. In large branches like Agbala Itura, monthly tithes and offerings have been estimated at over ₦10 million. Across its many branches nationwide and abroad, this number scales exponentially.
Corporate Tithing System
In 2003, CAC introduced a policy requiring individual assemblies to remit a percentage of their income to the central office. This system has created a steady and centralized stream of income, enabling the church to fund capital projects and support weaker branches.
Special Programs: Seed of Blessing and Sacrificial Offerings
These seasonal initiatives encourage members to give beyond their regular offerings. Funds raised during these events are often allocated to large-scale projects such as new church buildings, missionary work, or social impact programs.
Publications and Media Sales
CAC also earns revenue through the sale of religious books, CDs, DVDs, and other media resources. Since 1992, the church has streamlined this into a centralized system that supports its publishing ministry while contributing to its overall income.
5. International Presence and Global Impact
With active congregations in countries like the UK, Spain, and Tanzania, CAC’s influence and revenue streams are not confined to Nigeria alone. These foreign branches contribute financially through remittances and help broaden the church’s international visibility.
While CAC does not publicly disclose detailed financial reports, estimates from related denominations suggest significant worth. For instance, The Apostolic Church Nigeria (which shares early historical ties with CAC) was estimated to be worth over $8.33 million as of 2024. Given CAC’s broader operations and larger infrastructure, its net worth is believed to be even higher.
6. Challenges and Controversies
Despite its financial and spiritual success, CAC has not been without internal challenges and controversies.
Administrative Disputes
There have been reports alleging that church titles and leadership positions in some assemblies are influenced by financial contributions rather than spiritual merit. These claims, if true, raise questions about transparency and governance within the church hierarchy.
Doctrinal Variations and Breakaway Groups
As CAC continues to grow, so too have the number of independent branches and groups claiming affiliation. Some leaders have introduced practices that diverge from traditional CAC teachings, causing friction and debate within the larger CAC community.
Conclusion: A Legacy of Spiritual and Financial Growth
The wealth profile of Christ Apostolic Church paints a picture of an institution that has successfully balanced spiritual responsibility with strategic financial growth. From sprawling real estate developments to elite educational institutions, CAC has proven its ability to manage large-scale operations with discipline and purpose.
While challenges persist, the church’s strong leadership and loyal congregation continue to drive it forward. As CAC moves into its second century, maintaining transparency, accountability, and spiritual integrity will be key to preserving its remarkable legacy—for both the kingdom of God and the communities it serves.
Post A Comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *








































































































































0 Comments